Computer Vision
The use of technology in cricket has seen a significant increase in recent years, leading to overlapping computer vision-based research efforts. This study aims to extract front pitch view shots in cricket broadcasts by utilizing deep learning. The front pitch view (FPV) shots include ball delivery by the bowler and the stroke played by the batter. FPV shots are valuable for highlight generation, automatic commentary generation and bowling and batting techniques analysis. We classify each broadcast video frame as FPV and non-FPV using deep-learning models.
- Categories:
 89 Views
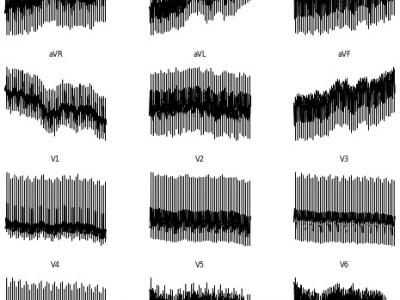
89 Views<p>Electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation is critical for diagnosing a wide range of cardiovascular conditions. To streamline and accelerate the development of deep learning models in this domain, we present a novel, image-based version of the PTB Diagnostic ECG Database tailored for use with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), vision transformers (ViTs), and other image classification architectures. This enhanced dataset consists of 516 grayscale .png images, each representing a 12-lead ECG signal arranged as a 2D matrix (12 × T, where T is the number of time steps).
- Categories:
 143 Views
143 Views
We evaluate the performance of our proposed method using four benchmark datasets: MNIST, CIFAR-10, Traffic-sign Recognition (TSR), and Room-occupancy Detection (ROD). Each dataset is divided into training and test sets, with specific proportions as described below.MNIST: This dataset consists of grayscale images of handwritten digits, with 10 distinct classes. It includes 60,000 training images and 10,000 test images, each formatted as a 28x28 pixel grayscale map.CIFAR-10: Unlike MNIST, CIFAR-10 is a dataset of color images.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets comprise images of 10 and 100 categories, respectively, with a fixed size of 32x32 pixels in color.
Tiny-ImageNet dataset consists of 200 categories with approximately 120,000 samples, where each class contains 500 training images, 50 validation images, and 50 test images, with each image sized at 64 x 64.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
The Tiny-ImageNet dataset contains 200 categories and approximately 120,000 samples. The CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets respectively contain 10 and 100 categories.
All experiments were conducted on a server equipped with two NVIDIA A100 GPUs (each with 80GB memory), running the Ubuntu 20.04 operating system and the CUDA 11.8 computing platform under the Pytorch 1.8 framework. The server has 256GB of memory and is powered by a 64-core Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6326 CPU @ 2.90GHz.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
To promote the development of camouflaged object detection technology, an visible-infrared artificial camouflage dataset (VIAC) is constructed. To simulate and replicate real-world scenarios, we customize and procure a set of metal models and camouflage materials to construct artificial camouflage environments. Utilizing DJI drones equipped with a dual-mode (visible and infrared) imaging system, we conduct coordinated aerial photography in complex outdoor settings, thereby comprehensively acquiring 1,500 pairs of high-quality visible and infrared images.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 ViewsSynthetic image data set using a generative model with explicit control over the head pose. HPGEN offers a promising solution to address data set bias in the head pose estimation as current benchmarks suffer from a limited number of images, imbalanced data distributions, the high cost of annotation, and ethical concerns.
- Categories:
 288 Views
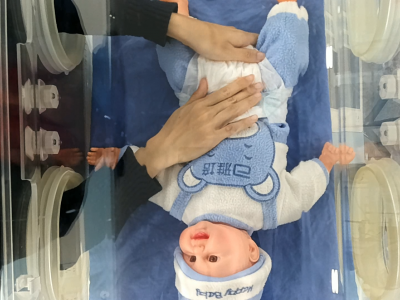
288 ViewsNICU-Care is a high-quality video dataset designed to support visual recognition tasks in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) scenarios, including nursing action recognition, object detection, and semantic segmentation. It was constructed in a standardized simulated NICU environment, capturing multi-view RGB videos of professional nurses performing six types of routine caregiving procedures on simulated infants. The dataset provides fine-grained temporal annotations and pixel-level segmentation masks for key objects like nurse hands, medical tools, and infant body parts.
- Categories:
 116 Views
116 Views
This dataset aims to support research on temporal segmentation of the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test using a first-person wearable camera. The data collection includes a training set of 8 participants and a test set of 60 participants. Among the 8 participants, the test was completed at both a normal walking pace and a simulated slower walking pace to mimic elderly movement patterns. The 60 participants were randomly divided into two groups: one group completed the test at a normal walking pace, and the other group simulated slower walking speed to mimic elderly movement patterns.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
Making images unlearnable through imperceptible perturbations is to prevent unauthorized image scraping from training deep neural networks (DNNs). Most existing methods for breaking these unlearnable data focus on applying image transformation techniques to disrupt the added perturbations, with limited attention given to modifying the classification tasks (target classes) of DNNs as an alternative approach. In this paper, we explore the vulnerabilities of unlearnable data, focusing mainly on modifying the classification tasks rather than applying image transformation techniques.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views